Titanium: Important Material in Medical Technology
Titanium is one of the most powerful and reliable materials in medical technology. What are titanium's characteristics that make it so special? And what is important when processing this material? Learn more about the characteristics and possible applications of titanium in medical technology.
Titanium: valuable properties, versatile applications
The use of titanium and titanium alloys represents a true revolution in the field of medical technology. The metal is now used in a wide variety of applications, for example in hip prostheses, skullcap plates or bone implants. This is due to the special properties of titanium, which make it an all-round talent among medical materials that meets the high demands of medical technology.
What properties does titanium have?
In addition to its high compatibility and extreme stability, titanium is particularly interesting for medical applications because of its elasticity. The coefficient of elasticity of the light metal is remarkably close to that of human bone and also exhibits exceptionally high fatigue strength. These properties are particularly important when titanium is used for implants for hip or knee joints and enable patients to regenerate more quickly after surgery.
Generally speaking, if implants are to remain in the human body for a long period of time, the materials must be biocompatible, corrosion-resistant, tissue-compatible and elastic. Titanium fulfils all these properties in full.
Medical applications for titanium materials
Titanium materials are used in almost every area of medicine – both unalloyed and alloyed. Currently, the material is used above average in the following disciplines in particular:
- Joint replacement parts for hip, knee, shoulder, spine, elbow, and hand
- Fixation materials for bones like nails, screws, nuts, and plates
- Dental implants and parts for orthodontic surgery and dental prosthetics
- Pacemaker housings and artificial heart valves
- Surgical instruments for heart and eye surgery
- Components in fast running blood centrifuges
- Walking aids and wheelchairs
Whether for hip prostheses, skullcap plates or bone or dental implants – no other material can be used in such a variety of ways. The exceptional properties of titanium materials not only make the biomaterial resilient, but also bio compatible and bio adhesive. This means that the body accepts the material without any problems, and tissue and bone cells can grow particularly well on the implant.
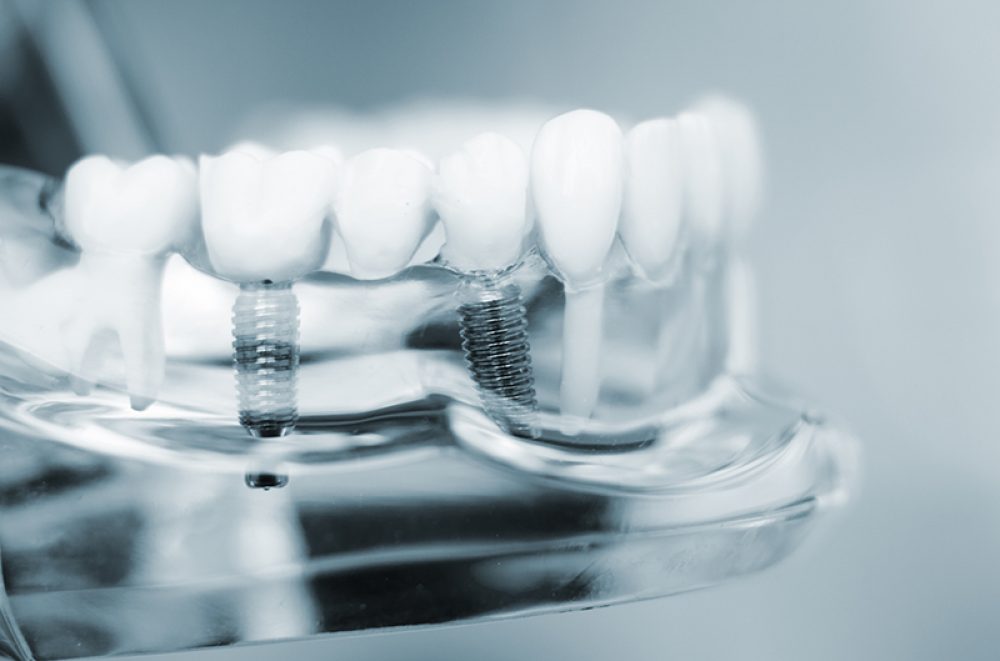
Titanium in dentistry
In dentistry, especially in dental prosthetics, such as crowns and bridges, titanium is the material of choice. This light metal is not only robust, but also tasteless, and its use is also associated with lower costs. In addition, the material is more resistant to corrosion, which provides a long-lasting feeling of safety when wearing dental implants.
Besides pure titanium materials, alloys are also used. One of the major developments in the field of alloys concerns the toxic element vanadium. It is replaced by elements that are compatible with the body, such as iron, as in the case of the titanium alloy TiAl 5Fe2.5. Due to its high purity, the alloy Ti6Al4V ELI is often used in the dental field.
Titanium in sports medicine
In accident surgery as well as in surgical orthopaedics and sports medicine, the robust light metal is now considered one of the most important materials. Titanium is also used in the treatment of bone fractures or serious head injuries – in different forms depending on the type of injury, for example by using titanium nails, for example in the case of bone fractures, or as plates in the case of injuries in the head area.
Other areas of application in medicine:
- The material is successfully used in middle ear surgery and in the creation of artificial stapes.
- In neurosurgery, clips made of titanium are used in aneurysm surgery. Titanium has largely replaced stainless steel due to its better NMR properties (NMR = Nuclear Magnetic Resonance).
- In food supplements and some drugs, titanium oxide is used as a colorant due to its good compatibility.
Titanium and medical progress
Internationally, scientists are researching new applications for titanium and titanium alloys. Research with the biomaterial is going in a variety of directions. Regarding implants, there are promising possibilities for further development – for example, by combining semi-flexible and solid materials. Another research goal is to make prostheses and implants even more compatible with the body.


