Hygrometers: Accurately Measuring Humidity
Too much or too little humidity can have a serious impact – on both health (think mold growth) and sensitive equipment. A hygrometer helps monitor humidity levels and, by extension, the integrity of buildings or stored goods – accurately and easily. But how exactly does a hygrometer work? What types are available? And what should you look for when choosing one? In this article, we’ll explore these questions and provide a clear overview. Let’s dive in!
What is a Hygrometer?
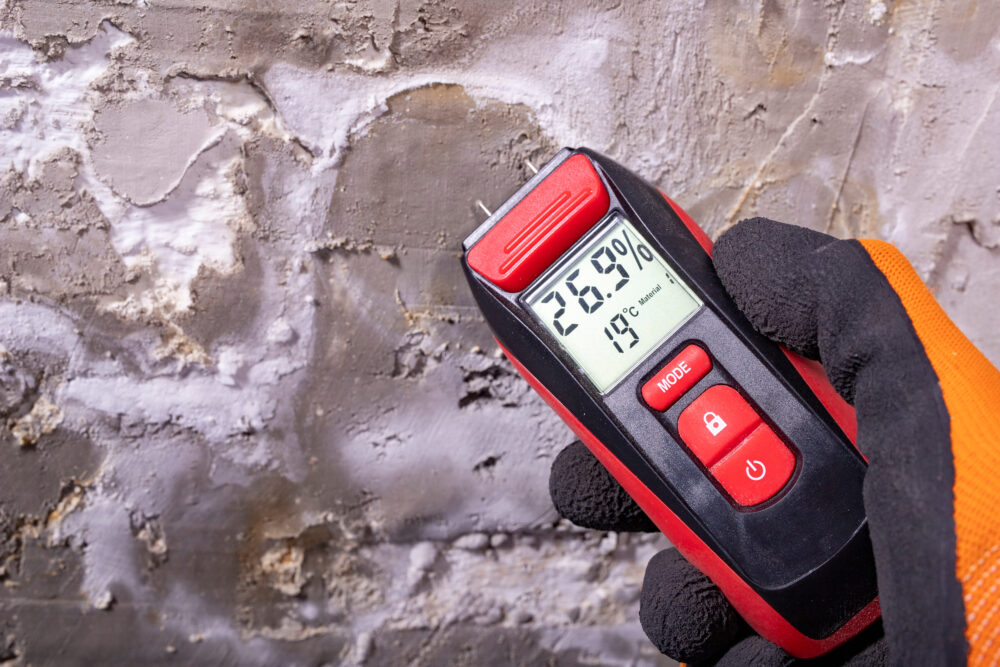
A hygrometer – also known as a humidity meter – is an instrument designed to measure the humidity level in the air. It’s used anywhere stable humidity is critical: homes, archives, production facilities, and laboratories. In HVAC systems, hygrometers are essential for maintaining an optimal indoor climate and ensuring proper air quality.
How is Humidity Measured?
Humidity can be measured in two ways: relative or absolute.
- Absolute humidity refers to the actual amount of water vapor in a given volume of air (grams per cubic meter).
- Relative humidity expresses this as a percentage, comparing the actual moisture content to the maximum amount the air can hold at a given temperature.
Modern hygrometers use high-performance sensors to measure humidity levels. Since warmer air can hold more moisture than cooler air, most devices also include a built-in thermometer to give context to the readings.
As a general guideline:
- 40–60% relative humidity is considered ideal for indoor spaces.
- Below 40%, mucous membranes may dry out, increasing the risk of infections.
- Above 70%, there’s a higher risk of mold formation, especially in poorly ventilated areas.
How Do Hygrometers Work?
Different types of hygrometers use different measurement principles. Bürklin Elektronik offers a wide range of compatible probes and sensors to suit your needs.
Mechanical (Analog) Hygrometers
Mechanical hygrometers rely on materials that expand or contract in response to humidity changes. A classic example is the hair hygrometer: a strand of natural or synthetic hair stretches as humidity increases and contracts as it decreases. This movement is transferred to a needle for easy reading – simple, reliable, and entirely energy-independent.
- Pros: No power source required
- Cons: Slower response time, limited accuracy, requires regular maintenance (calibration recommended every 6 months)
Electronic (Digital) Hygrometers
Digital hygrometers use sensors that operate based on resistive (ohmic) measurement principles. The electrical resistance changes with humidity levels, enabling precise readings. These devices deliver fast, accurate results and often come with extra features.
Many models include wireless capabilities, enabling integration into smart home systems or larger monitoring networks.
- Pros: High accuracy, digital display, data logging, connectivity (Bluetooth, wireless), no need for calibration
- Cons: Requires a power source
Combination Devices for Specialized Applications
Hygrometers are available in a variety of designs, including combination devices that integrate additional functions – such as thermometers, barometers, or clocks – for even greater versatility.
Where Are Hygrometers Used?
Hygrometers have a wide range of applications:
- Home use: Monitor indoor air quality, prevent mold growth, and maintain comfort
- Industrial environments: Manage humidity in sensitive production processes and protect workspaces from static buildup
- Labs & hospitals: Maintain strict environmental conditions required for certain processes and equipment
- Building technology: Control humidity in basements, warehouses, and other storage areas for sensitive goods like medicines or food
- Museums & archives: Protect artwork and historical documents from humidity damage
- Agriculture: Optimize ventilation and climate in greenhouses, storage facilities, etc.
Hygrometers in Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, precise humidity control is crucial – especially in sensitive manufacturing environments. For instance:
- In electronics production, hygrometers prevent static discharges caused by dry air.
- In the pharmaceutical and food industries, they help meet strict hygiene standards and ensure product quality.
- For raw material storage or facility management, they provide vital data for climate control.
Combined with other measurement instruments and sensors, hygrometers enable comprehensive monitoring systems – a key factor in process safety, energy efficiency, and product quality in the era of Industry 4.0.
Hygrometers: Small Devices, Big Impact
Whether you’re looking to improve indoor comfort or protect sensitive goods, a hygrometer provides the foundation for a healthy and stable environment. Modern electronic models, in particular, stand out for their precision and versatility. Regular monitoring helps detect problems early – so you can take action before damage occurs.