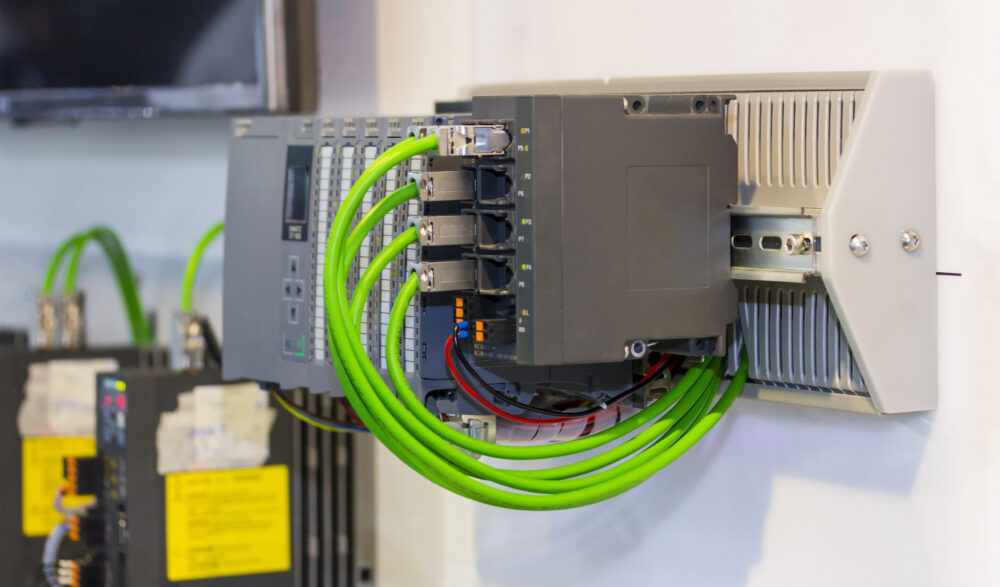
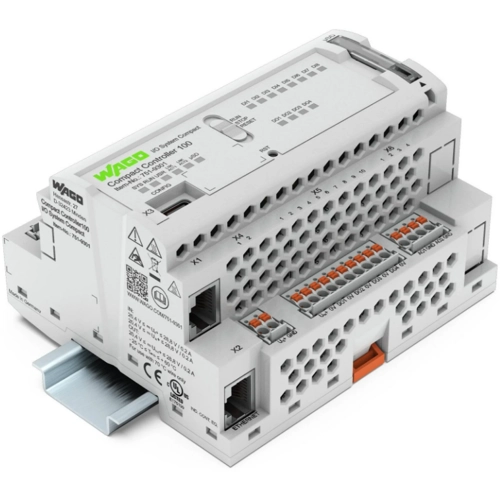
PLCs: The heart of modern automation
PLCs are an integral part of industrial automation. They control, regulate and monitor complex processes – from the production line to the packaging line. But what exactly is a PLC? What advantages does it offer? And how do modern PLC systems differ from one another? This article provides a comprehensive overview.
What is a PLC?
The abbreviation PLC stands for ‘programmable logic controller’. It is a digital, electronic system that automates industrial processes. Unlike traditional wiring solutions, a PLC can be flexibly programmed using a programming language such as Structured Text (ST), Ladder Diagram (LD) or Function Block Diagram (FBD).
A PLC essentially consists of three components:
- The central processing unit (CPU) processes inputs and controls outputs.
- Input modules detect signals from sensors, switches or other field devices.
- Output modules transmit control signals to actuators, motors or valves.
This gives the PLC a central role in control technology – fast, reliable and often under real-time conditions.
PLC or SPS? Two terms, one technology
In German-speaking countries, the term SPS is commonly used, whereas internationally, the term PLC – programmable logic controller – is more common. Technically, both mean the same thing: a system for the automated control of machines and systems. There are no differences; they are simply two terms for the same technology.
What can be programmed with a PLC?
PLC systems offer a wide range of applications in industrial automation. Typical areas of application are:
- Transport and assembly lines
- Machine control in manufacturing
- Process plants in chemical or food technology
- Robot control
- Building technology
Programming is usually done using standardised languages in accordance with IEC 61131-3. This standard simplifies the transition between manufacturers and enables a high degree of code reusability. Flexible programming is becoming increasingly important, especially in the context of Industry 4.0, as it is the only way to intelligently network machines and adapt them to changing requirements.
The advantages of modern PLC systems
Programmable logic controllers offer many advantages, especially when compared to conventional solutions with hard-wired logic:
- Flexibility: Program adjustments can be implemented quickly and without interfering with the hardware.
- Scalability: From small plants to complex systems, PLC solutions grow with your requirements.
- Reliability: PLC systems are robust, failure-proof and designed for continuous operation.
- Real-time capability: Many PLC controllers operate deterministically and are ideal for time-critical applications.
Thanks to these characteristics, PLCs have long been the standard in industrial control technology.
PLCs in the context of Industry 4.0
In the wake of Industry 4.0, the intelligent networking of machines, plants and IT systems is coming to the fore. PLC controls are the central hub in this context: they collect data from the field, evaluate it and initiate targeted actions – both locally and across the entire system in conjunction with ERP or MES systems.
Modern PLC systems now offer functions such as:
- Communication interfaces (e.g. Ethernet/IP, PROFINET, Modbus)
- Support for IoT protocols (e.g. MQTT)
- Integration into cloud platforms
- Diagnostic and remote maintenance functions
How do PLC controllers differ?
Not all PLCs are the same – depending on the complexity and requirements of a control task, there are various systems to choose from. Differences can be seen in the design, performance and area of application, among other things. The following overview compares the most important PLC variants and helps you find the right solution for your application.
| Type | Features | Area of application |
|---|---|---|
| Compact PLC | CPU, I/O and power supply integrated in one device | Small applications |
| Modular PLC | Individual components can be freely combined | Medium to large systems |
| Soft PLC / PC-based PLC | Software solution on industrial PCs | Flexible, performance-intensive applications |
| Logic modules | For simple control tasks, often preconfigured | Building technology, small machines |
Depending on the application, factors such as the number of I/Os, real-time requirements or network connection determine the choice of the right system.
Selection criteria for the right PLC
Choosing the right PLC is crucial for the smooth and efficient operation of your system. Requirements vary considerably depending on the application. From simple control tasks to highly complex processes with real-time requirements. To find the optimal solution, it is worth taking a closer look at the following points:
- How many inputs and outputs are required?
- Does the system need to be modularly expandable?
- Which communication interfaces are required?
- Are there any special requirements in terms of response times or environmental influences?
- Which software environments and programming languages are compatible?
Bürklin offers you a comprehensive range of PLC systems from leading manufacturers – tailored to a wide variety of industries, applications and budgets.
PLC – the control centre of industrial automation
Whether for simple control tasks or complex industrial processes, PLC controls offer a future-proof, powerful and flexible solution. In combination with Industrial Ethernet, IoT and cloud connectivity, they form the backbone of modern manufacturing concepts. Anyone looking to automate today cannot ignore PLCs.
Are you looking for the right control system for your application? At Bürklin, you will find a wide range of PLC systems, logic modules and accessories.