Patch Cables: The Invisible Heroes of Network Connectivity
Patch cables – inconspicuous yet indispensable for modern networks. They connect computers to routers, switches to servers, and ensure reliable data flow. With our guide, you'll find the perfect cable in 30 seconds.
Table of contents
- Your Patch Cable Quick Overview
- What is a Patch Cable?
- Patch Cable Configurator: 3 Clicks to the Perfect Cable
- CAT 5, CAT 6, CAT 7 and More: Which Do You Really Need?
- RJ45 Connectors: What You Need to Know
- Crossover or Straight-Through? Making the Right Choice
- Copper vs. Fiber Optic Patch Cables: The Quick Comparison
- Fiber Optic Patch Cables
- Custom Length Requirements: How Can I Crimp Patch Cables?
- Special Patch Cables for Special Requirements
- Frequently Asked Questions About Patch Cables
Your Patch Cable Quick Overview
| Application | Category | Speed | Range | Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Home Network | CAT 5e/6 | 1 Gbit | 100m | ✓ 250+ variants |
| Office/SME | CAT 6a | 10 Gbit | 100m | ✓ 180+ variants |
| Industrial | CAT 7/7a | 10 Gbit | 100m | ✓ 120+ variants |
| Data Center | CAT 8 | 40 Gbit | 30m | ✓ 45+ variants |
What is a Patch Cable?
Patch cables are pre-assembled network cables with RJ45 connectors that connect your devices and enable data exchange:
- Computer ↔ Router/Switch for internet connection
- Switch ↔ Patch panel in server room
- Device ↔ Network socket in office
The quality and specifications of the patch cable significantly impact network performance. Therefore, it’s important to select the right patch cable for your specific network requirements.
The 3 most important selection criteria:
- Speed: What data rate do you need?
- Length: 0.5m to 30m available
- Shielding: UTP (standard) or STP (shielded)
Our recommendation for beginners: CAT6 patch cable, 2-3m, UTP
Patch Cable Configurator: 3 Clicks to the Perfect Cable
Step 1: Where will you use the cable?
- Home: CAT5e/CAT6 sufficient
- Office: CAT6a recommended
- Server room: CAT7/CAT8 optimal
- Industrial: Shielded variants needed
Step 2: What length do you need?
- 0.5 – 1m: Patch panel connections
- 2 – 3m: Standard workstation
- 5 – 10m: Cross-room
- 15m+: Special applications
Good to know: Cable length affects transmission speed – the longer the cable, the lower the speed.
Step 3: Special requirements?
- PoE-capable for IP cameras/phones
- Flat for under-carpet installation
- Outdoor for exterior use
- Color-coded for server room
CAT 5, CAT 6, CAT 7 and More: Which Do You Really Need?
After the fundamental considerations for choosing the right patch cable, it is now time to look at the specific categories. From CAT 5, which is sufficient for standard home applications, to CAT 8, which is intended for professional networks – each category is designed for specific network environments.
CAT 5e – The Classic for Home Networks
The standard for network cables supports signal rates of up to 100 MHz and is suitable for gigabit operation. CAT 5 cables are sufficient for most home users.
- Speed: 1 Gbit/s
- Frequency: 100 MHz
- Ideal for DSL, cable internet, home network
CAT 6 – The All-Rounder
Frequently used in the professional sector, CAT 6 patch cables achieve operating frequencies of up to 250 MHz.
- Speed: 1 Gbit/s (10 Gbit up to 55m)
- Frequency: 250 MHz
- Ideal for small offices, gaming, streaming
- Future-proof: For the next 5-10 years
CAT 6a – The Professional Standard
CAT 6a patch cables support 500 MHz and are suitable for 10 Gigabit Ethernet.
- Speed: 10 Gbit/s
- Frequency: 500 MHz
- Ideal for enterprises, servers, NAS systems
- Special feature: Full 10 Gbit up to 100m
CAT 7/7a – Maximum Performance
CAT 7 patch cables are heavily shielded and reach operating frequencies of up to 600 MHz. CAT 7a even manages up to 1,000 MHz.
- Speed: 10 Gbit/s
- Frequency: 600 MHz (CAT7) / 1000 MHz (CAT7a)
- Ideal for data centers, broadcast
- Advantage: Best shielding (S/FTP)
CAT 8 – The Future
Mainly used in the professional sector, the high-quality CAT 8 cables achieve operating frequencies of up to 2,000 MHz.
- Speed: 25/40 Gbit/s
- Frequency: 2000 MHz
- Ideal for high-end data centers
- Limitation: Max. 30m range
Not sure? CAT6/6a is completely sufficient for 95% of applications!
RJ45 Connectors: What You Need to Know
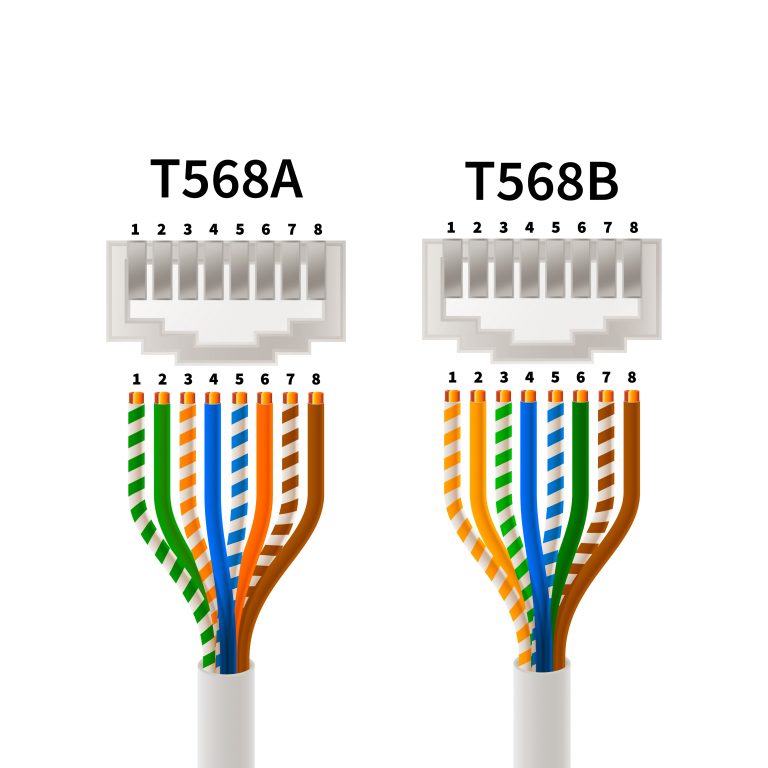

The correct patch cable wiring of RJ45 connectors is crucial. There are two wiring standards:
- T568A: European standard (white/green – green – white/orange – blue – white/blue – orange – white/brown – brown)
- T568B: US standard, but also widely used in Germany (white/orange – orange – white/green – blue – white/blue – green – white/brown – brown)
Important: Both standards work equally well. The key is to stick to one standard throughout your network!
For connector quality:
- Gold-plated contacts = better conductivity
- Strain relief = longer lifespan
- Latch protection = easy handling
There are special RJ45 variants for all possible applications, e.g.:
- RJ45 with LED: Shows network activity directly on the connector
- Flat RJ45: For tight passages
- Angled RJ45: Space-saving behind furniture
Crossover or Straight-Through? Making the Right Choice
In networking technology, we distinguish between two basic cable types that differ in their internal wiring. Straight-through cables (also called 1:1 cables) connect the pins identically at both ends – pin 1 to pin 1, pin 2 to pin 2, and so on. These cables are the standard for almost all modern network connections: computer to switch, switch to router, or device to network socket. They transmit the signal “straight through” without crossing.
Crossover cables, on the other hand, cross certain wire pairs: the transmit pins of one end are connected to the receive pins of the other end. These cables were once essential for directly connecting two similar devices, such as PC to PC or switch to switch. Without this crossing, both devices would transmit and receive on the same pins – communication would be impossible.
The good news: Thanks to Auto-MDI-X technology, which has been built into almost all network devices since about 2005, modern switches, routers, and network cards automatically detect which cable type is connected and adjust their internal wiring accordingly. This makes crossover cables practically obsolete today. For your network installation, this means: You can safely use straight-through cables for all connections – the devices handle the rest automatically.
Our tip: Invest exclusively in high-quality straight-through patch cables. These cover 100% of all modern use cases and save you from managing different cable types.
Copper vs. Fiber Optic Patch Cables: The Quick Comparison
Copper cables have proven themselves in many areas, but advancing technology and increasing network demands are bringing fiber optic cables increasingly into focus.
Copper Patch Cables
Advantages:
- Affordable
- PoE-capable
- Easy installation
- Up to 100m range
- Ideal for: 99% of all applications
Copper patch cables are an essential component of modern network infrastructures and offer clear advantages thanks to their specific properties, making them suitable for various applications. The pairwise twisting of copper strands in these cables minimizes electromagnetic interference (EMI), enabling stable and efficient data transmission.
The quality of the inner conductor plays a crucial role in signal integrity. High-quality copper ensures optimal signal quality and supports longer transmission distances. The flexibility of copper patch cables facilitates installation and maintenance. Their widespread compatibility with existing network devices and infrastructures are additional advantages, while their cost-effectiveness makes them an economical choice for many network applications.
Fiber Optic Patch Cables
Advantages:
- Highest speeds (100+ Gbit)
- Long ranges (up to 40km)
- No electromagnetic interference
- Future-proof
- Ideal for: Data centers, backbone
In addition to conventional copper cables, there are also fiber optic patch cables, which are distinguished by their advanced technologies. The low signal losses lead to more efficient and reliable data transmission, a clear advantage of fiber optic cables. In terms of robustness, fiber optic cables offer high resistance to external influences such as magnetic fields, moisture, and cold.
Their range is considerable, as they can reach lengths of up to 450 meters in combination with network installation cables. This makes fiber optic cables an excellent choice for extensive networks.
Additionally, the energy efficiency of fiber optic patch cables is high, as they consume less power. The use of fiber optic patch cables is therefore ideal in data centers, industrial facilities, and other demanding environments where high bandwidth and speed are required.
Custom Length Requirements: How Can I Crimp Patch Cables?
Need custom lengths? No problem with the right tools! To crimp patch cables, the copper wires of the cable are firmly pressed into the RJ45 connector to create a stable electrical connection. Ensure all components are of high quality for optimal performance and longevity.
What you need:

Special tools and materials are required for successful crimping of patch cables. In our “Crimping” guide, we have collected the most important information about crimping for you – from choosing the right tool to step-by-step instructions.
Special Patch Cables for Special Requirements
Patch cables play a vital role in modern infrastructure, ranging from cloud computing and IoT to Industry 4.0 and automated buildings:
- Cloud computing: In data centers and cloud environments, patch cables enable high-speed connections between servers and storage systems to ensure efficient data processing and storage.
- IoT: In the world of the Internet of Things (IoT), patch cables connect countless sensors and devices to collect and exchange data.
- Industry 4.0: In the automation and networking of production facilities, patch cables contribute to smooth communication between machines and control devices.
- Building automation: In intelligent buildings, patch cables enable the interconnection of lighting, heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) to save energy and increase comfort.
Special patch cables are the backbone of modern infrastructure:
Power over Ethernet (PoE)
Power and data over one cable – perfect for:
- IP cameras
- WLAN access points
- VoIP phones
Outdoor Patch Cables
Weatherproof and UV-resistant for:
- Security cameras
- Garden WLAN
- Building networking
- Outdoor cables with PE jacket
Flat Patch Cables
Only 1.5mm thick – ideal for:
- Under-carpet installation
- Through door gaps
- Space-saving installation
Bürklin Elektronik – Your trusted partner for patch cables
As your reliable partner, Bürklin Elektronik offers an extensive range of high-quality patch cables. We strive to offer you the best solutions for your particular requirements.
- Advice: Our experts will help you choose the right cable by considering your network requirements, the type of data and the bandwidth needed.
- Assembly: We can help you customize your patch solutions, whether you need a custom cable for a specific application or assistance filtering for your perfect fiber optic patch cable.
- Quality and customer satisfaction: We pride ourselves on our commitment to quality and customer satisfaction. Working with reputable manufacturers, we ensure that all our patch cables meet the highest standards.
Frequently Asked Questions About Patch Cables
What is the difference between CAT5, CAT6 and CAT7 patch cables?
The main difference lies in transmission speed and frequency. CAT5e supports up to 1 Gbit/s at 100 MHz frequency – sufficient for normal home networks. CAT6 also achieves 1 Gbit/s but operates at 250 MHz and can even manage 10 Gbit/s over short distances (up to 55m). CAT7 offers 10 Gbit/s at 600 MHz over the full distance of 100m and is fully shielded (S/FTP). For most applications, CAT6 is the best compromise between price and performance. CAT7 is only worthwhile for professional installations with high interference sources.
What is the maximum length for a patch cable?
The maximum length for Ethernet copper cables is 100 meters from device to device. This typically divides into 90 meters of permanently installed cable plus 10 meters of patch cable (2×5 meters at both ends). A single patch cable should not exceed 25 meters to avoid signal loss. For longer distances, you need to add a switch or switch to fiber optic. This rule applies equally to all CAT categories.
When do I need shielded patch cables (FTP/STP) instead of unshielded (UTP)?
Unshielded UTP cables are completely sufficient for normal office and home environments. They are more flexible, cheaper, and easier to install. You only need shielded cables (FTP/STP) in environments with strong electromagnetic interference sources: industrial halls with large motors, transmission systems, medical equipment, or when network cables are laid parallel to power cables. Important: Shielded cables must be properly grounded on both sides, otherwise they can actually pick up more interference than unshielded ones.
Which patch cable category do I need for PoE (Power over Ethernet)?
All cables from CAT5e upward work for PoE in principle. However, for optimal performance and heat dissipation, we recommend CAT6a or CAT7, especially for PoE++ (up to 100W). These have thicker copper conductors (AWG23 instead of AWG24), which reduces resistance and minimizes heat generation. CAT6a is the sweet spot for PoE applications: it supports all PoE standards, offers sufficient reserves, and is attractively priced. Look for cables with pure copper instead of copper-clad aluminum (CCA).
What do the colors of patch cables mean?
The cable color itself has no technical significance – you can use any color. However, many IT departments use color codes for organization: gray for standard workstations, red for servers, yellow for uplinks, blue for VoIP phones, green for guest WLAN. The wire colors inside the cable, however, follow fixed standards: T568A (common in Europe) or T568B (US standard). Both work equally well; what matters is consistent use throughout the network.
Can I mix CAT7 cables with CAT5e components?
Yes, you can mix different CAT categories – the network will work fine. But: Overall performance always follows the weakest link. If you connect a CAT7 cable to a CAT5e socket, the connection only works with CAT5e performance. For Gigabit Ethernet, this makes no difference, but the higher investment in CAT7 would be wasted. Our tip: Stick to one category or upgrade completely step by step.
What is AWG in patch cables and what gauge do I need?
AWG (American Wire Gauge) indicates the thickness of the copper conductors – the smaller the number, the thicker the wire. Standard patch cables have AWG24 (0.51mm diameter), high-quality cables AWG23 (0.57mm). Thicker conductors (AWG23) offer lower resistance, better signal quality, and less heat generation with PoE. AWG24 is sufficient for normal data cables; for PoE applications or lengths over 20m, we recommend AWG23. Beware of AWG26 or AWG28 – these thin cables are only suitable for very short connections.
Do I need special outdoor patch cables for outside use?
Yes, for outdoor areas you need special outdoor patch cables with PE jacket (polyethylene). Normal PVC cables become brittle from UV radiation and damaged by moisture. Outdoor cables are UV-resistant, waterproof, and temperature-stable from -40°C to +80°C. For underground cables, additionally choose rodent-proof variants with steel armoring. The alternative for temporary installations is to run normal cables in protective conduits.